Observations of the cosmic ray detector at the Argentine Marambio base in the Antarctic Peninsula
-
54 views
-
1 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
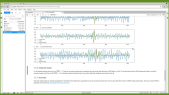
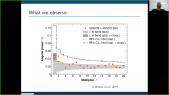
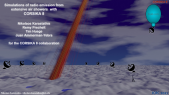
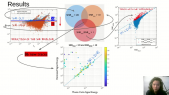
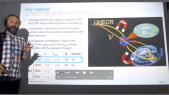
'In March 2019 a Space Weather Laboratory was deployed at Marambio base in the Antarctic Peninsula. The main instrument installed was a cosmic ray detector based on water Cherenkov radiation. This detector is the first permanent Antarctic node of LAGO (Latin American Giant Observatory) Collaboration and it has been working continously since its installation. LAGO Project is an extended Astroparticle Observatory and It is mainly oriented to basic research in three branches of Astroparticle physics: the Extreme Universe, Space Weather phenomena, and Atmospheric Radiation at ground level. The LAGO Space Weather program is directed towards the study of how the variations of the flux of secondary cosmic rays at ground level are linked with the heliospheric and geomagnetic modulations.rnrnObservations made during 2019 and 2020 will be presented here. The corrected count rate observed with our WCD is compared with observations of Oulu neutron monitor with similar rigidity cut off than the Marambio site (2,32 GV). During the summer Antarctic campaign of 2020 a new acquisition system was implemented. With this new system we are able to get a count rate related to the flux of secondary particles in a specific range of deposited energy into the detector. We analyze the effect of pressure and temperature in each of these count rates.'
Authors: Noelia Ayelén Santos
Co-Authors: Sergio Dasso | Adriana Gulisano | Omar Areso | Matías Pereira | Hernán Asorey | Lucas Rubinstein For the LAGO collaboration
Collaboration: LAGO
Indico-ID: 365
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/304
Noelia Ayelén Santos