Numerical Study the Corotating Interaction Region's effect on cosmic proton and helium
-
101 views
-
1 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 14. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/21-Short-term-modulation-SH/117
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-07/8
Abstract:
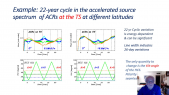
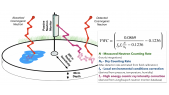
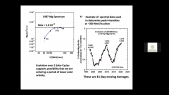
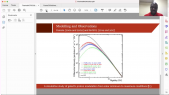
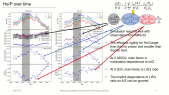
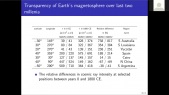
A Corotating Interaction Region (CIR) is formed when the fast solar wind catches the slow solar wind. It is known that the intensity of Galactic Cosmic Ray (GCR) is modulated by the CIR. Usually, the GCR intensity is suppressed inside the CIR. However, previous studies were mainly confined to GCR protons. In this study, we have utilized a hybrid GCR transport model, which incorporates the Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulated solar wind plasma background with CIR structure. Additionally, adopting appropriate mass, charge and Local Interstellar Spectra, the hybrid transport model is applied to both GCR proton and helium. It is found that (1) both proton and helium is modulated by the CIR so that their intensity is depressed, (2)however, the modulation level of proton and helium is different, and interestingly, the ratio of the proton and helium flux also varies with longitude.'
Authors: xi luo
Co-Authors: Marius Potgieter | Fang Shen | Weiwei Xu
Indico-ID: 1080
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1353
xi luo