Search for correlations between high-energy gamma rays and neutrinos with the HAWC and ANTARES detectors
-
90 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 4, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 21. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/24-Ground-based-measurements-of-low-energy-GCRs-SH/98
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-06/7
Abstract:
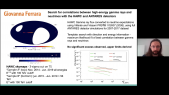
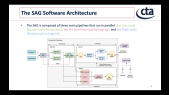
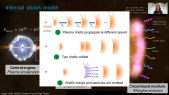
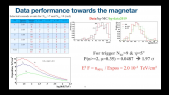
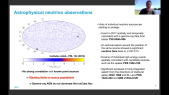
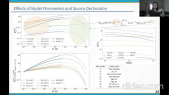
'ANTARES is an underwater neutrino detector in the Mediterranean Sea. Its location, reconstruction accuracy for all-flavor neutrino interactions, and low energy threshold, make it the most sensitive neutrino observatory for searches below 100 TeV over large parts of the sky. The HAWC experiment is a water Cherenkov gamma-ray detector located in Mexico. Thanks to its large field of view it is an excellent instrument to observe the very-high energy gamma-ray sky and perform high-sensitivity surveys of the Galactic Plane.rnThe 10-year ANTARES data set and 3-year HAWC point source surveys are used to search for all- flavor neutrino emission in correlation with the highly-significant observations by HAWC in the gamma-ray sky by means of a maximum-likelihood template search. No significant observation for a correlation has been identified and upper limits on the neutrino flux from the HAWC observations have been set.'
Authors: Giovanna Ferrara | for the ANTARES Collaboration | for the HAWC Collaboration
Co-Authors: Luigi Antonio Fusco
Collaboration: AntaresHAWC
Indico-ID: 967
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/962
Giovanna Ferrara