Search for dark matter from the center of the Earth with 8 years of IceCube data
-
65 views
-
1 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
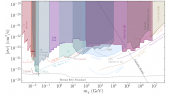
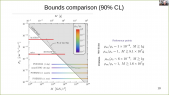
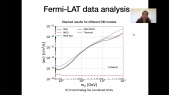
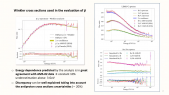
'The nature of Dark Matter remains one of the most important unresolved questions of fundamental physics. Many models, including the Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs), assume Dark Matter to be a particle and predict a weak coupling with Standard Model matter. If Dark Matter particles can scatter off nuclei in the vicinity of a massive object, such as a star or a planet, they may lose kinetic energy and become gravitationally trapped in the center of such objects, including Earth. As Dark Matter accumulates in the center of the Earth, self-annihilation of WIMPs into Standard Model particles can result in an excess of neutrinos which are detectable at the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, situated at the geographic South Pole. A search for excess neutrinos from these annihilations has been performed on 8 years of IceCube data, and results have been interpreted in the context of a number of WIMP annihilation channels (χχ➝τ+τ-/W+W-/bb̅) and masses ranging from 10 GeV to 10 TeV. We present the latest results from this analysis and compare the outcome with previous analyses by IceCube and other experiments, showing competitive results, which are even world-leading in some parts of the phase space.'
Authors: Giovanni Renzi
Collaboration: IceCube
Indico-ID: 639
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/526
Giovanni Renzi