Time-dependent treatment of cosmic-ray spectral steepening due to turbulence driving
-
141 views
-
5 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/12-Galactic-Particle-Acceleration-including-PIC-CRI-CRD-MM/127
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-03/4
Abstract:
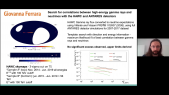
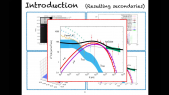
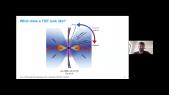
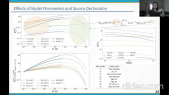
"Cosmic-ray acceleration at non-relativistic shocks relies on scattering by turbulence that the cosmic rays drive upstream of the shock. We explore the rate of energy transfer from cosmic rays to non-resonant Bell modes and the spectral softening it implies. Accounting for the finite time available for turbulence driving yields a much smaller spectral impact than found earlier with steady-state considerations. Generally, for diffusion scaling with the Bohm rate by a factor $eta$, the change in spectral index is at most $eta$ divided by the Alfv'enic Mach number of the thermal sub-shock. For small $M_mathrm{A}$ it is well below this limit. Only for very fast shocks and very efficient cosmic-ray acceleration the change in spectral index may reach $0.1$. For standard SNR parameters it is negligible."
Authors: Martin Pohl
Indico-ID: 52
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/987
Martin Pohl